Production Practices and Profitability of Artisanal Fishing in Warri South West LGA, Delta State, Nigeria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60787/gjmsti.vol1no1.51Keywords:
Production practices, Profitability,, Artisanal,, FishersAbstract
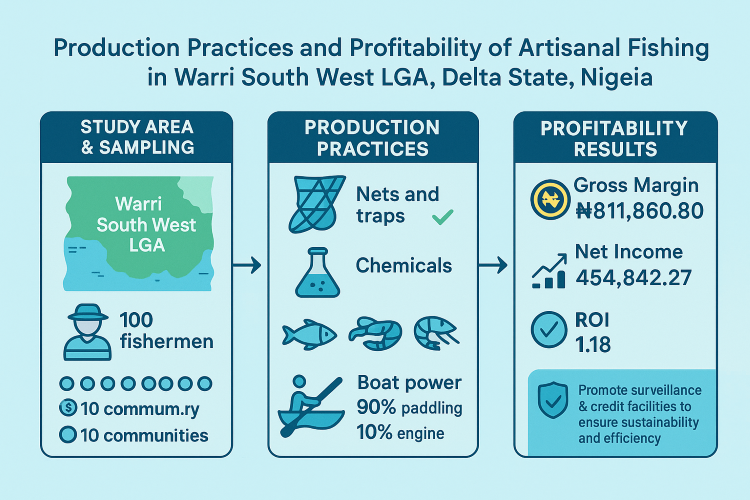
Artisanal fishing is essential for providing many people with nutrition, employment, and livelihood. However, as water pollution and the blue economy continue to increase, it is crucial to determine if the production practices of artisanal fishing are harmful to the water bodies. This study, conducted between February and May, 2019, closely examines the production practices and profitability of artisanal fishing in Warri South West Local Government Area of Delta State, Nigeria. A two-stage sampling procedure was employed to ensure a comprehensive investigation, beginning with purposive sampling of ten communities where artisanal fishermen were predominant. The second stage involved randomly selecting ten fishermen from each of the ten communities, resulting in a total sample size of 100 artisanal fishermen. Data were analyzed using tables, means, percentages, gross margin, net income, and returns on investment. Results indicate that all fisherfolk use only nets and traps to capture their products. Additionally, 90% of the fishers use hand paddling to power their canoes and harvest more than one type of aqiatic species. Gross margin, net income, and returns on investment were found to be N811,860.80, N454,842.27, and 1.18, respectively. This study suggests that proper surveillance should be implemented to prevent fishers from using harmful methods, such as chemicals, and to prevent overfishing to ensure the sustainability of artisanal fishing and improve efficiency among fisherfolks.